Use webhooks
Learn how to integrate webhook signals to be automatically informed when a document is processed or more.
Webhooks are used to get status updates on the current document workflow status. Most often they are used to be informed if a document was uploaded, automatic extraction is finished and of course the document itself is set to "status" = "done".
After login into the Parashift Platform, you will find webhooks in the "Development" section. You can configure your own webhooks depending on your use case.
Set the webhook URL and optional headers that will be included with all requests. The optional headers can be used to implement token-based authentication. To this end, add a custom Authorization header using an API Bearer (or any other value) token recognised by your webhook endpoint.
Configuration & Test
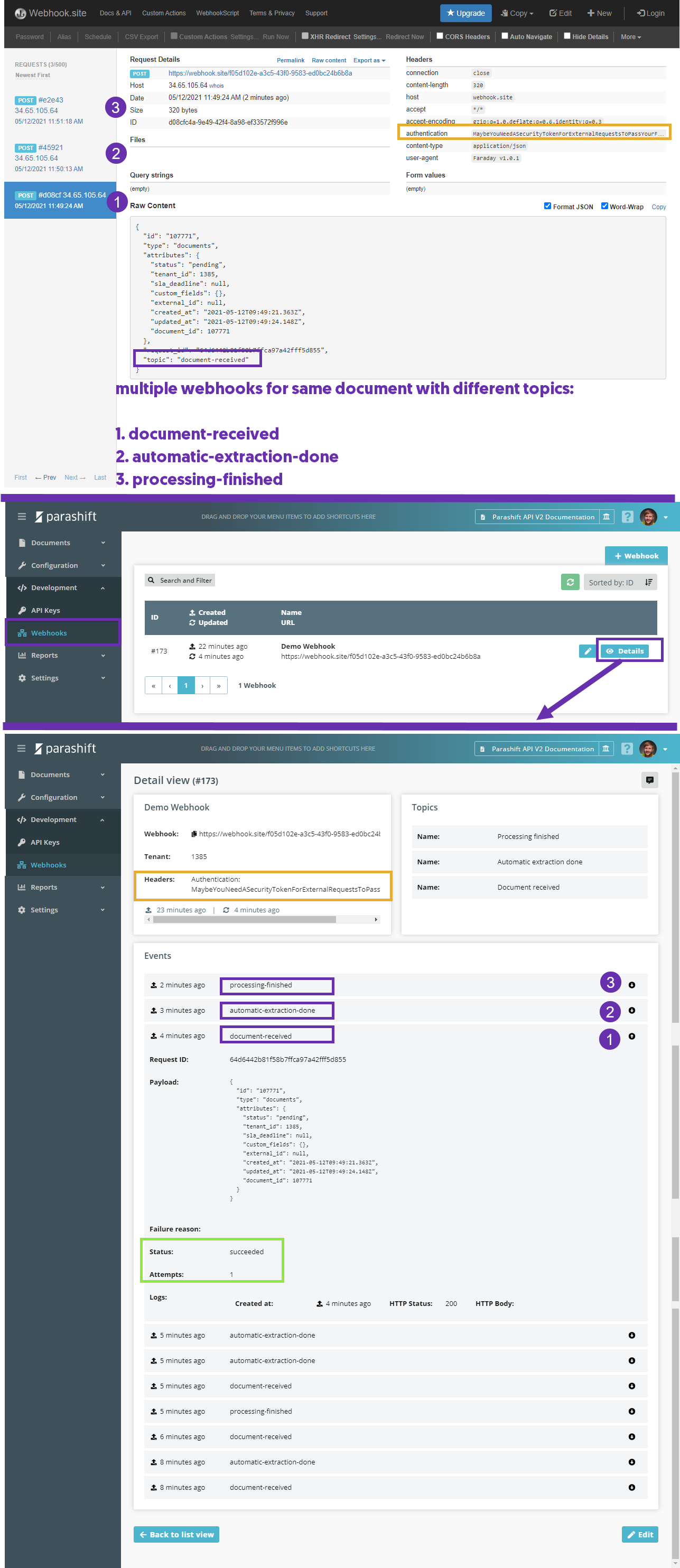
- Open the Parashift Platform and navigate in the main menu to Development / Webhooks
- Change an existing webhook.
- Add a webhook.
- Enter a webhook name (organization / beauty only) and the webhook URL to which the webhook is sent. Please make sure that this URL is publicly available!
If you only want to test webhooks you can use e.g. https://webhook.site/ where you can get a temporary public URL that is listening for webhooks. (Parashift is not affiliated with that site, it just proofed to be very useful to test, use at your own risk) - Optional: define your own Authorization headers
- Define when a webhook should be triggered (see chapter "Topics" below for more details.


To test your webhook configuration simply upload a document and guide it through the workflow until your desired topic (e.g. document_received) is triggered.
Following an example of multiple successfull sent webhooks for one document with different topics.
Purple: all three webhook topics were triggered and reached their destination URL
Orange: the configured headers were passed through to the external URL
Green: If a webhook should not reach it's destination the webhook is retriggered multiple times with an exponential backoff strategy.
Payload
The payload of a delivered webhook contains the document id and status information on the processing of the requested document. By design, we don't include any information that we deem "sensitive". If you used "custom_fields" or the "external_id" on upload these are also included.
If you want to get the full document, check out how to request a document.
https://docs.parashift.io GET "Show document"
{
"id": "107786",
"type": "documents",
"attributes": {
"status": "pending",
"tenant_id": 1385,
"sla_deadline": null,
"custom_fields": {
"SomeCustomField": "These custom fields cannot be queried.",
"AnotherCustomField": "If you want to query for an external ID please use external_id.",
"YetAnotherCustomField": "external_id can be queried and used for lookups to get your data back."
},
"external_id": "EX123456789",
"created_at": "2021-05-12T10:05:46.229Z",
"updated_at": "2021-05-12T10:05:46.302Z",
"document_id": 107786
},
"request_id": "ef083852541ff078340a516432aee2f4",
"topic": "document-received"
}
Missing Webhooks / overdue documents
Even though we are using an exponential backoff strategy to send undelivered webhooks multiple time over steadily increasing time intervals it can still happen that a webhook is lost.
Please make sure to always have a backup strategy to regularly pull for the status of document's that exceed certain time limits.
E.g. if you expect a document to be processed by the machine in 60 seconds and you have not received a webhook after 5 minutes it can make sense to pull for the data of this document to see that the document did not fail or indeed was processed bu the webhook did not make it.
Topics
| Workflow | Title (in app) | Value (in payload) |
|---|---|---|
| Inbound | DOCUMENT RECEIVED | document-received |
| PREPROCESSING DONE | preprocessing-done | |
| Separation | AUTOMATIC SEPARATION DONE | automatic-separation-done |
| READY FOR SEPARATION 1ST LEVEL | ready-for-separation-first-level | |
| READY FOR SEPARATION 2ND LEVEL | ready-for-separation-second-level | |
| READY FOR SEPARATION 3RD LEVEL | ready-for-separation-third-level | |
| READY FOR SEPARATION QC | ready-for-separation-qc | |
| SEPARATION DONE | separation-done | |
| Classification | AUTOMATIC CLASSIFICATION DONE | automatic-classification-done |
| READY FOR CLASSIFICATION FIRST LEVEL | ready-for-classification-first-level | |
| READY FOR CLASSIFICATION SECOND LEVEL | ready-for-classification-second-level | |
| READY FOR CLASSIFICATION THIRD LEVEL | ready-for-classification-third-level | |
| READY FOR CLASSIFICATION QC | ready-for-classification-qc | |
| CLASSIFICATION DONE | classification-done | |
| Extraction | AUTOMATIC EXTRACTION DONE | automatic-extraction-done |
| READY FOR EXTRACTION FIRST LEVEL | ready-for-extraction-first-level | |
| READY FOR EXTRACTION SECOND LEVEL | ready-for-extraction-second-level | |
| READY FOR EXTRACTION THIRD LEVEL | ready-for-extraction-third-level | |
| READY FOR EXTRACTION QC | ready-for-extraction-qc | |
| EXTRACTION DONE | extraction-done | |
| Outbound | PROCESSING FINISHED | processing-finished |
| PROCESSING FAILED | processing-failed |
Retries & Exponential Backoff
Webhooks use an 'exponential backoff' strategy to optimize reliability. When a webhook delivery fails due to network or server issues, we don't immediately retry. Instead, we wait briefly and then progressively increase the time between retries. This approach prevents overloading your system, increasing the chances of successful webhook delivery without straining your infrastructure.
| Retry attempt | seconds delay |
| 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 32 |
| 3 | 243 |
| 4 | 1024 |
| 5 | 3125 |
| 6 | 7776 |
| 7 | 16807 |
| 8 | 32768 |
IP Range
We always send webhooks from the following range of IP addresses. This is useful if you want to restrict incoming traffic.
34.65.0.0/16